The Income Tax Act, 1961, lays out stringent rules to limit cash transactions limits and promote transparency, while also discouraging tax evasion. If you’re a taxpayer or business owner, it’s crucial to understand these rules to avoid hefty penalties. Here’s a concise guide to the key cash transaction limits you need to be aware of:

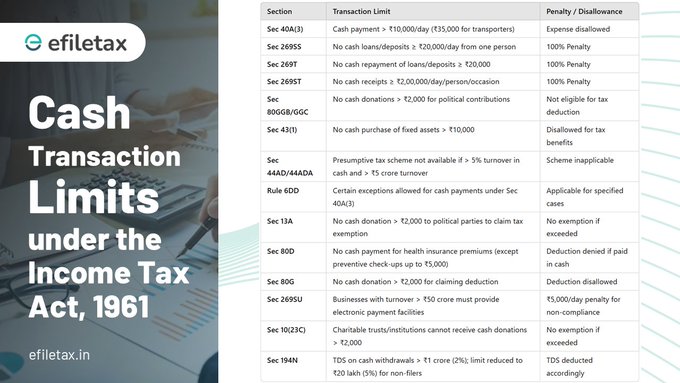
1. Section 40A(3): Restrictions on Business Expenses
Cash payments exceeding ₹10,000 per day to a single person for business expenses are disallowed as a deduction. For payments to transporters, the limit is set at ₹35,000.
2. Section 269SS: Cash Loans or Deposits
No person can accept loans or deposits in cash of ₹20,000 or more from a single person. Violating this provision leads to a penalty equal to the amount accepted.
3. Section 269T: Repayment Restrictions
Repaying loans or deposits in cash ₹20,000 or more is not permitted. A penalty equivalent to the repaid amount is levied for non-compliance.
4. Section 269ST: Cash Receipt Limit
Receiving ₹2,00,000 or more in cash from a person, whether in a single day, a single transaction, or on an occasion, is prohibited. Non-compliance attracts a 100% penalty on the amount received.
5. Section 80GGB & 80GGC: Donations to Political Parties
Cash donations exceeding ₹2,000 to political parties are not eligible for deductions. This provision aims to bring more transparency to political funding.
6. Section 43(1): Purchase of Fixed Assets
Cash payments above ₹10,000 for acquiring fixed assets are excluded from the cost of the asset, meaning no depreciation benefits can be claimed.
7. Section 44AD/44ADA: Presumptive Taxation Restrictions
Under presumptive taxation schemes, cash receipts must not exceed 5% of total turnover or gross receipts. If breached, the presumptive scheme becomes inapplicable.
8. Rule 6DD: Exceptions to Cash Payments
There are certain exceptions under Rule 6DD for payments exceeding limits under Section 40A(3), including payments made to the government, payments under exceptional circumstances, or in areas lacking banking facilities.
9. Section 13A: Political Party Donations
Political parties cannot accept cash donations exceeding ₹2,000 to claim tax exemptions.
10. Section 80D: Health Insurance Premiums
Cash payments for health insurance premiums do not qualify for deductions, except for preventive health check-ups up to a limit of ₹5,000.
11. Section 80G: Charitable Donations
Donations made in cash above ₹2,000 are not eligible for deductions under Section 80G.
12. Section 269SU: Electronic Payment Facility
Businesses with turnover exceeding ₹50 crore are required to offer electronic payment facilities. Non-compliance can lead to a penalty of ₹5,000 per day.
13. Section 10(23C): Charitable Institutions
Charitable institutions must avoid cash donations exceeding ₹2,000 to claim tax exemptions.
14. Section 194N: TDS on Cash Withdrawals
Banks are required to deduct 2% TDS on cash withdrawals exceeding ₹1 crore in a financial year. For non-filers of income tax returns, the threshold is reduced to ₹20 lakh with 5% TDS.
Cash Transaction Limits under the Income Tax Act, 1961
Stay Within Cash Transaction Limits to Avoid Penalties
The restrictions on cash transactions are designed to curb tax evasion and promote digital transactions. Understanding these limits helps you stay compliant and avoid penalties. Ensure that any high-value transactions are conducted through banking channels, particularly for business expenses, loans, donations, and withdrawals.
Did you find this guide helpful? For more insights and professional assistance on tax matters, reach out to efiletax today.